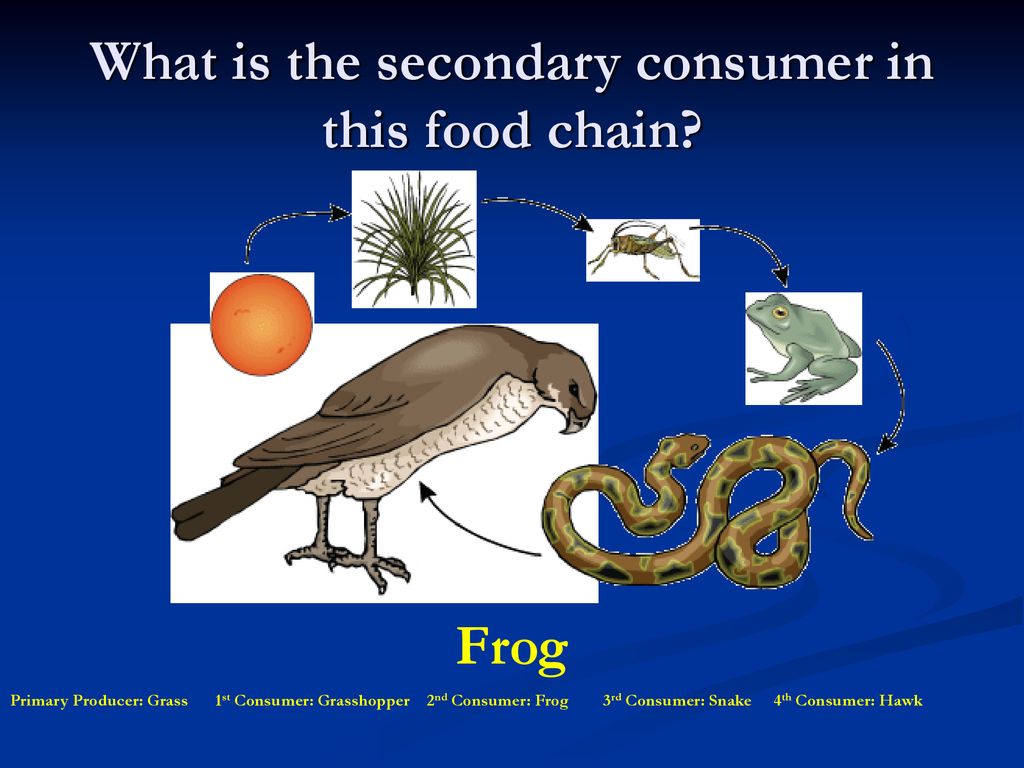
Ecology 101 PowerPoint Presentation free download Biology Diagrams
Ecology 101 PowerPoint Presentation free download Biology Diagrams Secondary consumers are placed at the third trophic level in the food chain. These are organisms that eat primary consumers for nutrients & energy purposes. It shows the flow of energy from one trophic level to another. A trophic level is a feeding level in a food chain. Secondary Consumers Types. Three main types of consumers can be found
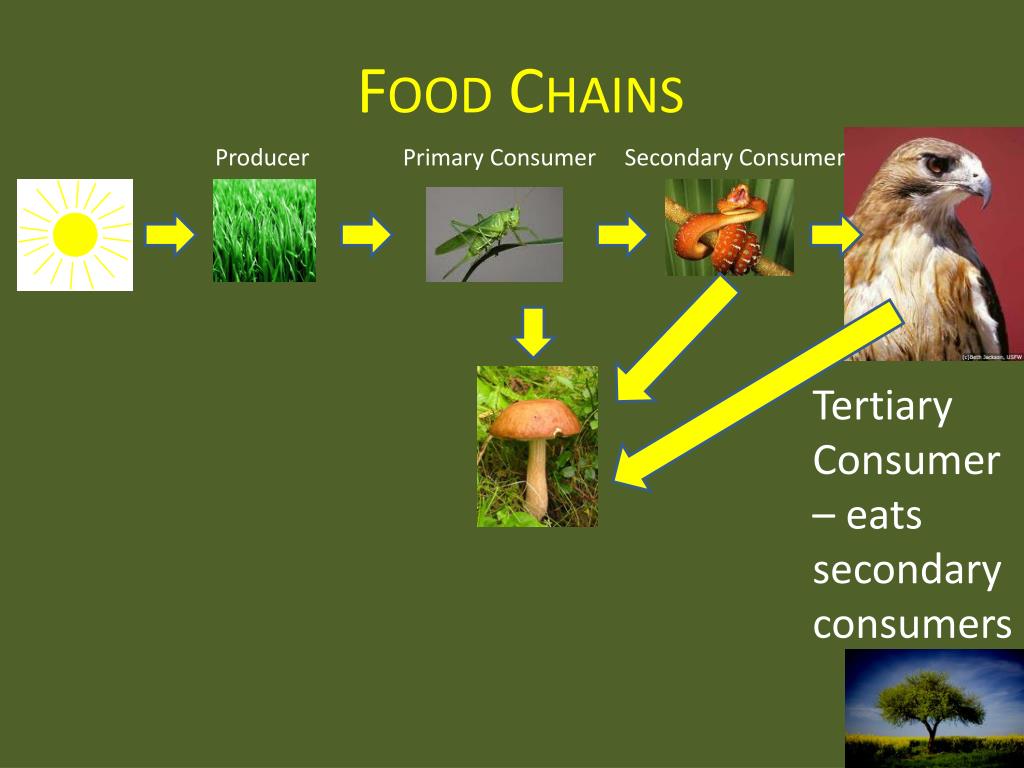
Secondary consumers often serve as prey for tertiary consumers, thus linking various levels of the food chain and promoting nutrient cycling. Role in Ecosystem Resilience In a healthy ecosystem, secondary consumers contribute to its resilience by preventing any single species from dominating the landscape.
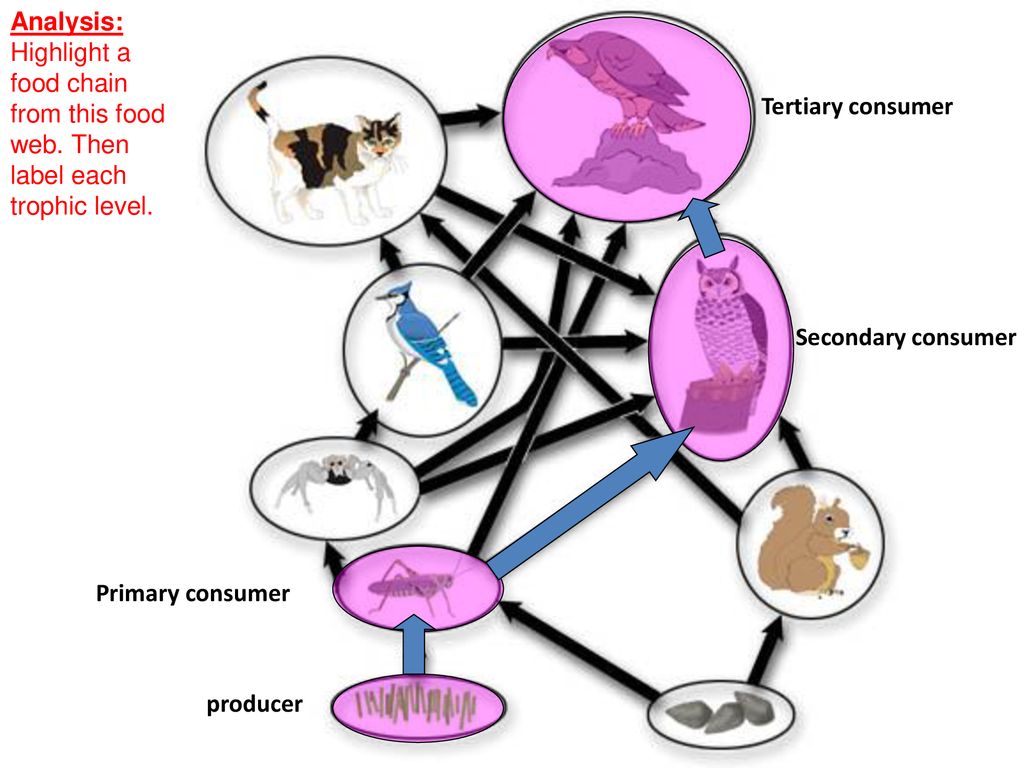
Secondary Consumer: Definition, Examples, Functions Biology Diagrams
Secondary Consumers in the Tropic Pyramid. Secondary consumers play a crucial role in the trophic pyramid. The trophic pyramid is a visual representation of the distribution of energy and biomass and consists of different trophic levels, with each level representing a step in the food chain.

What are Secondary Consumers? Secondary consumers play a crucial role in ecological systems, serving as a key link in the energy transfer process within a food chain. These organisms primarily obtain their energy and nutrients by feeding on primary consumers, which are typically herbivores that consume plants.The position of secondary consumers is at the third level in a food chain's trophic

Definition and Examples Biology Diagrams
Secondary consumers occupy the third trophic level in a typical food chain.They are organisms that feed on primary consumers for nutrients and energy. While primary consumers are always herbivores; organisms that only feed on autotrophic plants, secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores. Carnivores eat only animals, but omnivores eat both animals and plants.